An overview of Pertussis
What is Pertussis?
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory infectioncaused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It Pertussis spreads easily fromperson to person mainly through droplets produced by coughing or sneezing. Thedisease is most dangerous in infants, and is a significant cause of disease anddeath in this age group.
While whooping cough can affect people at any age, it can be deadly for infants andyoung children.According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC),before a vaccine was available, whooping cough was a major cause of childhood deathsin the United States. The CDC reports the total number of cases of pertussis in 2016was just under 18,000, with 7 deaths reported.
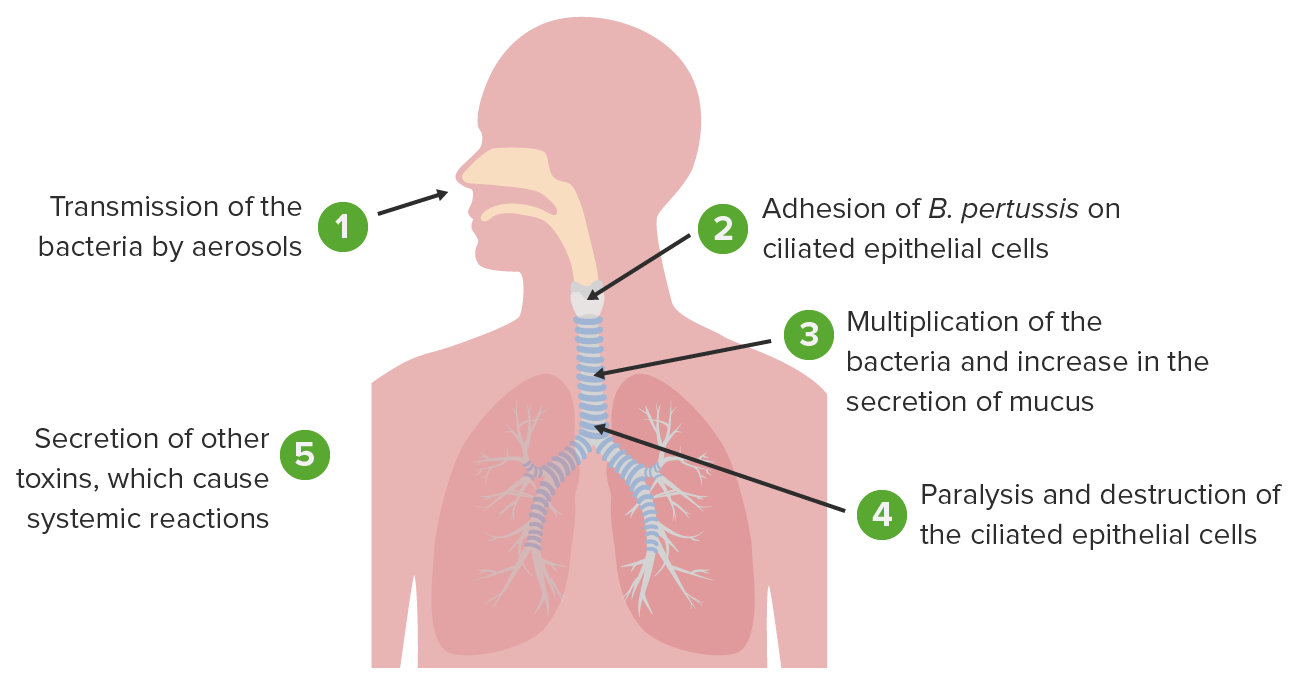
Causes of Pertussis
Pertussis (Whooping cough) is caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetellapertussis. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, tiny germ-laden droplets aresprayed into the air and breathed into the lungs of anyone who happens to be nearby.
In most cases, a person contracts pneumonia-causing pathogens by breathing them intothe small air sacs, or alveoli, within their lungs. The immune system responds bysending white blood cells to attack the infection, which triggers inflammation ofthe alveoli. The alveoli fill with fluid and pus, causing pneumonia.
Signs and symptoms of Pertussis?
Once you become infected with whooping cough, it takes about seven to 10 days forsigns and symptoms to appear, though it can sometimes take longer. They're usuallymild at first and resemble those of a common cold:
1. Runny nose
2. Nasal congestion
3. Red, watery eyes
4. Fever
5. Cough
After a week or two, signs and symptoms worsen. Thick mucus accumulates inside yourairways, causing uncontrollable coughing. Severe and prolonged coughing attacks may:
1. Provoke vomiting
2. Result in a red or blue face
3. Cause extreme fatigue
4. End with a high-pitched "whoop" sound during the next breath of air
However, many people don't develop the characteristic whoop. Sometimes, a persistenthacking cough is the only sign that an adolescent or adult has whooping cough.
Infants may not cough at all. Instead, they may struggle to breathe, or they may eventemporarily stop breathing.
How can I prevent pertussis?
The best way to prevent whooping cough is to get vaccinated. Tdap, a pertussisbooster shot, is recommended for unvaccinated adults instead of their next Td(tetanus and diphtheria) booster, which is given every 10 years.
The effectiveness of vaccines decreases over time. Adults who were vaccinated againstpertussis as children can get whooping cough as their immunity, or protectionagainst the disease, begins to fade.
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider if you think you may have comeinto contact with someone with whooping cough, even if you haven’t developed achronic cough.
How is pertussis diagnosed?
To diagnose pertussis(whooping cough), your doctor will perform a physical exam andtake samples of mucus in the nose and throat. These samples will then be tested forthe presence of the B. pertussis bacteria. A blood test may also be necessary tomake an accurate diagnosis.
How is pertussis treated?
Many infants and some young children will need to be hospitalized during treatment,for observation and respiratory support. Some may need intravenous (IV) fluids fordehydration if symptoms prevent them from drinking enough fluids.
Since whooping cough is a bacterial infection, antibiotics are the primary course oftreatment. Antibiotics are most effective in the early stages of whooping cough.They can also be used in the late stages of the infection to prevent it fromspreading to others.
While antibiotics can help treat the infection, they don’t prevent or treat the coughitself.
However, cough medicines aren’t recommended — they have no effect on whooping coughsymptoms and may carry harmful side effects for infants and small children.
Most doctors suggest using humidifiers in your child’s bedroom to keep air moist andhelp alleviate symptoms of whooping cough.