An overview of Bronchitis
What is Bronchitis?
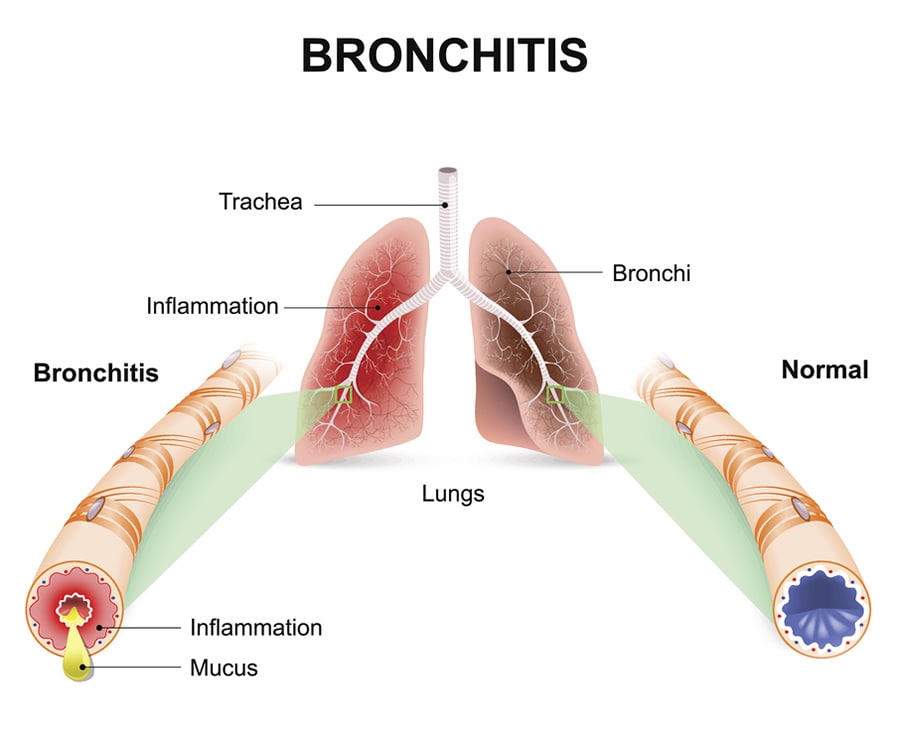
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which carry airto and from your lungs. People who have bronchitis often cough up thickened mucus,which can be discolored. Bronchitis may be either acute or chronic.
When your airways (trachea and bronchi) get irritated, they swell up and fill withmucus, causing you to cough. Your cough can last days to a couple of weeks. It’s themain symptom of bronchitis.
Types of Bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis : Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral infection andgoes away on its own in a few weeks. Most people don’t need treatment for acutebronchitis.
Chronic bronchitis : You have chronic bronchitis if you have a cough withmucus most days of the month for three months out of the year. This goes on for atleast two years.
Causes of bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is usually caused by viruses, typically the same viruses that causecolds and flu (influenza). Antibiotics don't kill viruses, so this type ofmedication isn't useful in most cases of bronchitis.
The most common cause of chronic bronchitis is cigarette smoking. Air pollution anddust or toxic gases in the environment or workplace also can contribute to thecondition.
Signs and symptoms of bronchitis?
A persistent cough that lasts one to three weeks is the main symptom of bronchitis.You usually bring up mucus when you cough with bronchitis, but you might get a drycough instead. You might also hear a whistling or rattling sound when you breathe(wheezing).
You might have other symptoms, including:
1. Shortness of breath (dyspnea).
2. Fever.
3. Runny nose.
4. Tiredness (fatigue).
5. Chest discomfort
How can I prevent bronchitis?
It is not always possible to prevent acute or chronic bronchitis, but several thingscan reduce the risk.
These include:
1. avoiding or quit smoking
2. avoiding lung irritants, such as smoke, dust, fumes, vapors, and air pollution
3. wearing a mask to cover the nose and mouth when pollution levels are high
4. washing the hands often to limit exposure to germs and bacteria
5. asking about vaccinations to protect from pneumonia and the flu
How is bronchitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can tell if you have bronchitis based on your health historyand symptoms (clinical diagnosis). They’ll listen to your lungs for signs ofcongestion and to make sure you’re breathing well. They might test you for viralinfections, like the flu or COVID-19.
How is bronchitis treated?
Acute bronchitis is usually not treated with medications. If you have the flu andyour symptoms started within the past two days, your provider may prescribeantivirals to help it go away faster.Since bronchitis is almost never caused bybacteria, antibiotics won’t help you get better and might even make you feel worse.
You can use medications to help you with symptoms or to treat the underlying cause,including:
Antiviral medications : If your bronchitis is caused by the flu, yourhealthcare provider might prescribe an antiviral medication, like Tamiflu®, Relenza®and Rapivab®. If you start taking antivirals quickly after your symptoms start, youmight feel better sooner.
Bronchodilators : Your provider might prescribe a bronchodilator (a drug thathelps open your airways) if you’re having trouble breathing.
Anti-inflammatory medications : Your doctor might prescribe corticosteroidsand other medications to reduce inflammation.
Cough suppressants : Over-the-counter or prescription cough suppressants(antitussives) may help with a nagging cough. This includes dextromethorphan(Robitussin®, DayQuil™, PediaCare®) and benzonatate (Tessalon Perles®, Zonatuss™).
Antibiotics : It’s very unlikely that you’ll be treated with antibiotics forbronchitis, unless your healthcare provider thinks you have a bacterial infection.
COPD/asthma treatment : If you have COPD or asthma, your provider may useadditional medications or breathing treatments for chronic bronchitis.
Frequently Asked Questions About bronchitis
When your airways are irritated, your immune systemcauses them to swell up and fill with mucus. You cough to try toclear the mucus out. As long as there’s mucus or inflammation inyour airways, you’ll keep coughing.
Bronchitis itself — inflammation of your airways —isn’t contagious, but the viruses and bacteria that can cause itare. For instance, if you’re sick with the flu, you might getbronchitis too. But when your friend gets the flu from you,their airways don’t get inflamed like yours did.
You can get bronchitis with almost any virus,including SARS-CoV2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Thesymptoms of bronchitis can be similar to COVID-19, so make sureyou get tested to know which one you have. There haven’t beenany studies that show that COVID-19 is any more likely to causebronchitis than other viral illnesses.
Yes, acute bronchitis usually goes away on its own.It’s almost always caused by a virus, and you can’t get rid ofmost viruses with medicine. You can treat the symptoms at homewhile you wait for the inflammation to go down.Bronchitis causedby something else may need treatment to help it go away. Chronicbronchitis usually doesn’t go away completely, but can getbetter with treatment.