An overview of Vaginitis
What is Vaginitis?
Vaginitis is an inflammation of the vagina that can result in discharge, itching andpain. It’s due to an imbalance of yeast and bacteria that normally live in thevagina.
Along with discomfort, you may notice a smell that's different than usual. You couldhave an infection caused by bacteria, yeast, or viruses. Chemicals in soaps, sprays,or even clothing that come in contact with this area could be irritating thedelicate skin and tissues.
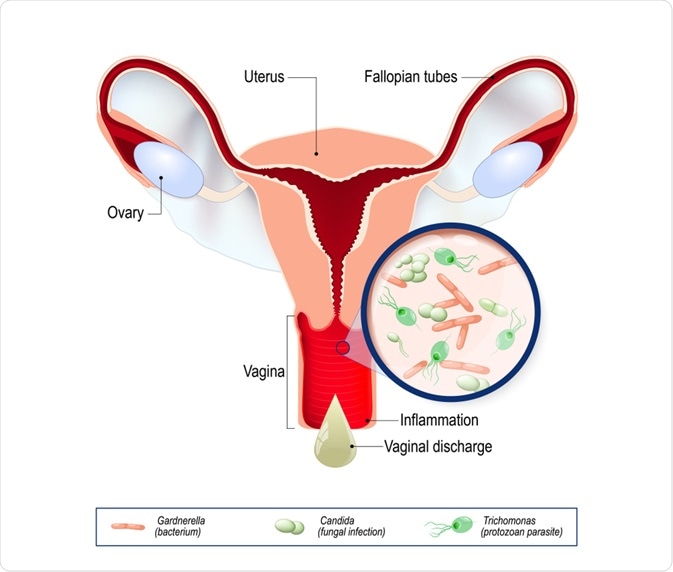
What are the most common types of vaginitis?
Bacterial vaginosis : inflammation of the vagina due to an overgrowth ofbacteria. It typically causes a strong fishy odor.
Candida or "yeast" infection : an overgrowth of the fungus candida, which isnormally found in small amounts in the vagina.
Chlamydia : is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in women,usually in those ages 18 to 35 who have multiple sex partners.
Gonorrhea : is another common infection spread through sex. It often comesalong with chlamydia.
Trichomoniasis : is an infection spread by sex that’s caused by a parasite. Itraises your risk for other STIs.
Viral vaginitis : is inflammation caused by a virus, like the herpes simplexvirus (HSV) or human papillomavirus (HPV), which spread through sex. Sores or wartson the genitals can be painful.
Causes of vaginitis
The cause depends on what type of vaginitis you have:
Bacterial vaginosis : This most common type of vaginitis results from a changeof the bacteria found in your vagina, upsetting the balance. What causes theimbalance is unknown. It's possible to have bacterial vaginosis withoutsymptoms.This type of vaginitis seems to be linked to but not caused by sex —especially if you have multiple sex partners or a new sex partner — but it alsooccurs in women who aren't sexually active.
Yeast infections : These occur when there's an overgrowth of a fungal organism— usually Candida albicans — in your vagina. C. albicans also causes infections inother moist areas of your body, such as in your mouth (thrush), skin folds and nailbeds. The fungus can also cause diaper rash.
Trichomoniasis : This common sexually transmitted infection is caused by amicroscopic, one-celled parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. This organism spreadsduring sex with someone who has the infection.In men, the organism usually infectsthe urinary tract, but often it causes no symptoms. In women, trichomoniasistypically infects the vagina, and might cause symptoms. It also increases women'srisk of getting other sexually transmitted infections.
Noninfectious vaginitis : Vaginal sprays, douches, perfumed soaps, scenteddetergents and spermicidal products can cause an allergic reaction or irritatevulvar and vaginal tissues. Foreign objects, such as toilet paper or forgottentampons, in the vagina also can irritate vaginal tissues.
Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (vaginal atrophy) : Reduced estrogenlevels after menopause or surgical removal of your ovaries can cause the vaginallining to thin, sometimes resulting in vaginal irritation, burning and dryness.
Signs and symptoms of Vaginitis
1. Change in color, odor or amount of discharge from your vagina
2. Vaginal itching or irritation
3. Pain during sex
4. Painful urination
5. Light vaginal bleeding or spotting
If you have vaginal discharge, the characteristics of the discharge might indicatethe type of vaginitis you have. Examples include:
Bacterial vaginosis : You might develop a grayish-white, foul-smellingdischarge. The odor, often described as a fishy odor, might be more obvious aftersex.
Yeast infections : The main symptom is itching, but you might have a thickwhite discharge that resembles cottage cheese.
Trichomoniasis : An infection called trichomoniasis (trik-o-moe-NIE-uh-sis)can cause a greenish-yellow, sometimes frothy discharge.
How can I prevent Vaginitis?
Keep yourself clean and dry. But doctors don't recommend vaginal sprays or heavilyperfumed soaps for this area. Douching may cause irritation, too, and, moreimportantly, could hide or spread an infection. It also removes the healthy bacteriathat do the housekeeping in your vagina. Douching is never recommended.
Avoid clothes that hold in heat and moisture. Nylon underwear, tight jeans, gymshorts and leggings that don’t breathe, and pantyhose without a cotton panel canlead to yeast infections.
Condoms are the best way to prevent passing infections between sexual partners.
Get a complete gynecologic exam every year, including a Pap smear if your doctorrecommends it.
How is vaginitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will take a thorough medical history, complete a physicalexam and swab the inside of your vagina to collect a fluid sample. They will sendthe sample off to a lab where the cells can be checked for signs of vaginitis. Yourhealthcare provider may check the PH levels of your vaginal fluid to get closer to adiagnosis.
Some providers may ask that you abstain from sex for 24 hours before yourappointment.
How is Vaginitis treated?
The key to treating vaginal infections is getting the right diagnosis.
Pay close attention to exactly which symptoms you have and when. Be ready to describethe color, texture, smell, and amount of discharge. Don't douche before your officeor clinic visit; it will make accurate testing hard or impossible. Some doctors willask you to not have sex during the 24 to 48 hours before your appointment.
It's better to see your doctor before you try over-the-counter medications, even ifyou're pretty sure you know what you have.
You treat noninfectious vaginitis by dealing with the probable cause. Consider whatproducts you're using that could be irritating your sensitive skin. For hormonalchanges, your doctor may prescribe estrogen to ease symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vaginitis
It isn’t a good idea to wait for vaginitis todisappear unless you know what’s causing it. For instance, somemild yeast infections go away on their own, but not all casesdo. Bacterial vaginosis usually clears up on its own, but leftuntreated, it can put you more at risk for STIs. It can alsocause complications if you’re pregnant. The symptoms from viralvaginitis may resolve on their own, but in the meantime, yourprovider needs to know about any STIs you have so they canmonitor any cell changes. Some kinds of high-risk HPV can leadto cervical cancer.
Vaginitis is uncomfortable, but finding the cause andthe right treatment can bring you relief. If chemical irritantsare causing your vaginitis, you can improve your symptoms byavoiding the offending lotion, detergent, spray, etc. Bacterialand antifungal medications may take up to two weeks to clearyour infection. Antiviral medications for viral vaginitis can’tcure the virus, but they can cause your symptoms to go awayfaster. Getting the right diagnosis and treating all causes ofyour vaginitis is key when it comes to relieving your symptoms.
Your vagina normally produces a discharge that’susually clear or slightly cloudy, non-irritating and with verylittle odor. During your menstrual cycle, the amount andconsistency of discharge changes. At one time of the month,there may be a small amount of a very thin or watery discharge.At another time (usually the latter part of the menstrualcycle), a more extensive thicker discharge may appear. All ofthese descriptions could be considered normal.A vaginaldischarge that has an odor or that is irritating is usuallyconsidered an abnormal discharge. The irritation might feelitchy or burning, or both. The burning could feel like a bladderinfection. The itching may be present at any time of the day,but it is often most bothersome at night. These symptoms oftenare made worse by sexual intercourse.
The sexually transmitted infections that causevaginitis are contagious. Trichomoniasis, chlamydia, herpes andHPV all spread person-to-person through sex. Getting infectedcan lead to vaginal inflammation and irritation associated withvaginitis. Bacterial vaginosis isn’t contagious, but havingunprotected sex with multiple partners may put you at greaterrisk of getting it.
Vaginitis isn’t a sexually transmitted infection, butsome sexually transmitted infections can cause vaginitis.Trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes and HPV are alltransmitted through sexual contact. And all of them can lead tovaginal inflammation and pain associated with vaginitis. But sexisn’t the only way you can get vaginitis. Bacterial vaginosis,yeast infections, non-infectious vaginitis and atrophicvaginitis are all types of vaginitis that aren’t consideredSTIs.