An overview of Neurodevelopmental disorders
What is Neurodevelopmental disorders?
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders that affect the development of the nervous system, leading to abnormal brain function which may affect emotion, learning ability, self-control, and memory. The effects of neurodevelopmental disorders tend to last for a person's lifetime.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are impairments of the growth and development of the brain and/or central nervous system. A narrower use of the term refers to a disorder of brain function that affects emotion, learning ability, self-control and memory which unfolds as an individual develops and grows.
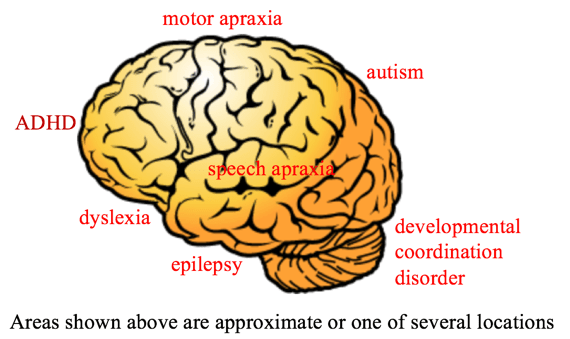
Type of Neurodevelopmental disorders
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
DLD - Developmental language disorder (formerly known as SLI- Specific Language Impairment)
Communication, speech, or language disorders, expressive language disorder, fluency disorder, social (pragmatic) communication disorder, and speech sound disorder.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
Intellectual disabilities (IDs) or intellectual development disorder (IDD, previously called mental retardation) and global developmental delay (GDD)
Motor disorders including developmental coordination disorder, stereotypic movement disorder, and tic disorders (such as Tourette's syndrome), and CAS - Apraxia of speech
Neurogenetic disorders, such as Fragile X syndrome, Down syndrome,[4] Rett syndrome, hypogonadotropic hypogonadal syndromes
Specific learning disorders, like dyslexia or dyscalculia.
Traumatic brain injury (including congenital injuries such as those that cause cerebral palsy[6]) and disorders due to neurotoxicants including Minamata disease caused by mercury, behavioral disorders including conduct disorder etc. caused by other heavy metals, such as lead, chromium, platinum etc., hydrocarbons like dioxin, PBDEs and PCBs, medications and illegal drugs, like cocaine, radioactive metals like Po210(which is found in cigarettes), and others.
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) can exhibit a combination of the above, most commonly ADHD, because of this, FASD is usually under-diagnosed, yet it is estimated that about 1 in 20 people may be affected
Causes of Neurodevelopmental disorders
The development of the nervous system is tightly regulated and timed; it is influenced by both genetic programs and the environment. Any significant deviation from the normal developmental trajectory early in life can result in missing or abnormal neuronal architecture or connectivity.[15] Because of the temporal and spatial complexity of the developmental trajectory, there are many potential causes of neurodevelopmental disorders that may affect different areas of the nervous system at different times and ages. These range from social deprivation, genetic and metabolic diseases, immune disorders, infectious diseases, nutritional factors, physical trauma, and toxic and environmental factors. Some neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism and other pervasive developmental disorders, are considered multifactorial syndromes which have many causes that converge to a more specific neurodevelopmental manifestation.
Signs and symptoms of Neurodevelopmental disorder
Symptoms of NDs are dependent on the ND, but general descriptions usually consist of impairments with the following;
1. Memory .
2. Language.
3. Behavior .
4.Motor skills .
5. Learning.
6. Speech
7. Social skills
8. Emotions
Neurodevelopmental disorders Diagnosis
Neurodevelopmental disorders are diagnosed by evaluating the presence of characteristic symptoms or behaviors in a child, typically after a parent, guardian, teacher, or other responsible adult has raised concerns to a doctor.
Neurodevelopmental disorders may also be confirmed by genetic testing. Traditionally, disease related genetic and genomic factors are detected by karyotype analysis, which detects clinically significant genetic abnormalities for 5% of children with a diagnosed disorder. As of 2017, chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) was proposed to replace karyotyping because of its ability to detect smaller chromosome abnormalities and copy-number variants, leading to greater diagnostic yield in about 20% of cases.[23] The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend CMA as standard of care in the US.
How are Neurodevelopmental disorder treated?
There aren't many treatment options for those with NDs, but research has determined some effective interventions. Although there is no cure for NDs there are methods that help with managing and coping with symptoms.
Behavioral Therapy
Therapies like applied behavioral analysis (ABA), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), speech therapy, and developmental therapy have all been shown to be beneficial for ND symptoms. CBT, Psychotherapy, and other behavioral therapies are utilized for adults with NDs like ADHD. ABA has a significant impact on behavior in children with NDs, especially ASD and ADHD.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a stimulation therapy that is commonly used for depression, but research trials have found prospects for rTMS to offer benefits for those with NDs. In a review of multiple studies, rTMS didn’t appear to have any severe adverse effects for children and adolescents with NDs.
rTMS treatment improved social functioning and behaviors for some participants with ASD. There were also benefits in those with tic disorders, in which treatment helped lessen tics. Unfortunately, rTMS did not show prospects for those with ADHD; it caused some irritation, hyperactivity, and inattentiveness in some individuals. Overall, rTMS has the potential to be an acknowledged treatment method for a few NDs.
Medication
Medication is sometimes prescribed to both children and adults with NDs. For ADHD, specifically, physicians may prescribe medication to help in managing symptoms like hyperactivity, agitation, inattentiveness, etc. Medication may consist of stimulants, antidepressants, or other pharmaceuticals suited to enhance cognition.
Medication, however, should not be the first choice when treating NDs like ADHD and AS. Experts express trying therapies and other strategies before medication. For pediatric patients, researchers suggest neurodevelopmental therapies and parenting training before incorporating medication into treatment routines.
Conventional and Alternative Medicine (CAM)
Nutrition, physical exercise, and recreational activities can also play a role in managing symptoms of NDs. It is important to develop healthy lifestyle habits for children and adults with NDs.
Complementary and alternative (CAM) medicines like supplements and mind/body practices, such as acupuncture, yoga, etc., are other options that are explored before seeking medication or are used along with medication
Adults with NDs most seek out these types of interventions. The national percentage of adults who engage in CAM treatment is 36-38%, but the number of children who participate in CAM treatment is unclear. A population review reported 11.8% of children throughout the population experienced CAM therapy at least once, but this number may not be accurate. It was stated in another report that the amount of children that engage in CAM treatment is between 2%-55%, but this is not a population report.
Frequently Asked Questions About Neurodevelopmental disorders
Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition which is usually diagnosed in the first 3 years of life. Generally parents become concerned when their child has delays in speech development, limited social relatedness, and restricted interests and activities. The child may avoid direct eye contact and exhibit odd behaviors such as focusing on parts of objects (e.g. the spinning wheel of a toy car). There may be unusual motor movements such as hand flapping, self stimulation or walking on toes.
There are no specific treatments to “cure” autism. Each child with an autism spectrum disorder has a unique constellation of developmental delays, speech deficits, social and cognitive impairments. Therefore, comprehensive treatment plans need to be developed to target each child's unique profile of strengths and functional impairments.
Abnormal development of the central nervous system