An overview of Stroke
What is Stroke?
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident or CVA isa serious life-threatening medical condition that affectsthe brain. It occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygenand nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot orbursts, And when that happens, part of the brain cannot getthe blood,oxygen and nutrient it needs, so that part of thebrain and it's cells begin to die. Annually over 13 millionpeople worldwide suffer from stroke. Of these, 5 million dieand another 5 million are left permanently disabled. It isthe fifth leading cause of death.A person experiencing astroke needs immediate emergency treatment.
Types of stroke?
Ischemic stroke: This is the most common type of stroke,making up 87% of all cases. It occurs when the blood supplyto part of the brain is interrupted or reduced by bloodclots, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen andnutrients.These blood clots typically form in areas wherethe arteries have been narrowed or blocked over time byfatty deposits known as plaques.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or Ministroke: This is atype of stroke that lasts only a few minutes, it occurs whenthe blood supply to a part of the brain is inadequate for ashort period of time. After a while blood supply resumesback to normal and it often resolve without treatment.
Hemorrhagic stroke: They're caused by a weakened vessel thatruptures and bleeds into the brain or it's surrounding andas a result, the part of the body controlled by the damagedarea of the brain cannot work properly.it make up about 13 %of stroke cases.
Causes of stroke
It can be caused by a narrowed blood vessel, bleeding, or aclot that blocks blood flow.
1. High blood pressure or hypertension:This is the biggestcause of strokes. If your blood pressure is typically 130/80or higher,then you need to see a doctor immediately todiscuss treatment
2. Heart disease: This condition includes defective heartvalves as well as atrial fibrillation, or irregularheartbeat, which causes a quarter of all strokes among thevery elderly. You can also have clogged arteries from fattydeposits.
3. Diabetes: People who have it often have high bloodpressure and are more likely to be overweight. Both raisethe chance of a stroke. Diabetes damages your blood vessels,which makes a stroke more likely. If you have a stroke whenyour blood sugar levels are high, the injury to your brainis greater.
4. High cholesterol levels.
5. Obesity.
6. Excessive alcohol intake.
7. Smoking.
Signs and symptoms of stroke
Trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying.You may experience confusion, slur words or have difficultyunderstanding speech.
Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm or leg. You maydevelop sudden numbness, weakness or paralysis in the face,arm or leg. This often affects just one side of the body.Try to raise both your arms over your head at the same time.If one arm begins to fall, you may be having a stroke. Also,one side of your mouth may droop when you try to smile.
Headache. A sudden, severe headache, which may beaccompanied by vomiting, dizziness or altered consciousness,may indicate that you're having a stroke.
Problems seeing in one or both eyes. You may suddenly haveblurred or blackened vision in one or both eyes, or you maysee double.
Trouble walking. You may stumble or lose your balance. Youmay also have sudden dizziness or a loss of coordination.
Some people may also experience: bladder or bowel controlproblems, depression, paralysis or weakness on one or bothsides of the body, difficulty controlling or expressingtheir, Symptoms vary and may range in severity.
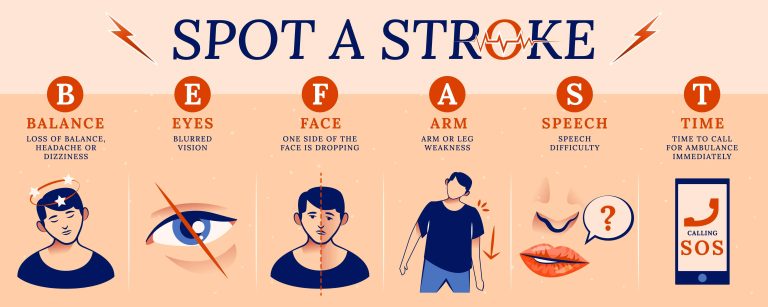
The fastest way to detect stroke is by using the acronynFAST which goes thus
Face: Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the facedroop?
Arms: Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm driftdownward? Or is one arm unable to rise?
Speech: Ask the person to repeat a simple phrase. Is his orher speech slurred or strange?
Time: If you observe any of these signs, call 911 oremergency medical help immediately.
Preventive measures against stroke
controlling your blood pressure levels
Maintaining a moderate weight
Managing diabetes
Eating a healthful diet including taking plenty fruits,vegetables, whole grains, nuts and seeds legumes
Exercising regularly
Avoiding alcohol, or only drinking moderately
Getting treatment for heart disease
Don't smoke
Diagnosis
Stroke begins rapidly, It are usually diagnosed by doingphysical tests and studying images of the brain producedduring a scan.
There are several different diagnostic tests a doctor canuse to determine the type of stroke. These include:
1. Physical examination: A doctor will ask about theperson’s symptoms and medical history. They will checkmuscle strength, reflexes, sensation, vision, andcoordination. They may also check blood pressure, listen tothe carotid arteries in the neck, and examine the bloodvessels at the back of the eyes.
2. Blood tests: A doctor may perform blood tests todetermine if there is a high risk of bleeding or bloodclots, measuring levels of particular substances in theblood, including clotting factors, and checking whether ornot an infection is present.
3. CT scan: A CT scan is like an X-ray, but uses multipleimages to build up a more detailed 3-dimensional picture ofyour brain to help your doctor identify any problem areas.During the scan, you may be given an injection of a specialdye into one of the veins in your arm to help improve theclarity of the CT image and look at the blood vessels thatsupply the brain. If it's suspected you're experiencing astroke, a CT scan is usually able to show whether you havehad an ischaemic stroke or a haemorrhagic stroke. It'sgenerally quicker than an MRI scan and can mean you're ableto receive appropriate treatment sooner.
4. MRI scan: An MRI scan uses a strong magnetic field andradio waves to produce a detailed picture of the inside ofyour body. It's usually used in people with complexsymptoms, where the extent or location of the damage isunknown. It's also used in people who have recovered from atransient ischaemic attack (TIA). This type of scan showsbrain tissue in greater detail, allowing smaller, or moreunusually located, areas affected by a stroke to beidentified. As with a CT scan, special dye can be used toimprove MRI scan images.
5. Carotid ultrasound: A doctor may carry out an ultrasoundscan to check blood flow in the carotid arteries and to seeif there is any narrowing or plaque present.
6. Cerebral angiogram: A doctor may inject a dye into thebrain’s blood vessels to make them visible under X-ray orMRI. This provides a detailed view of the blood vessels inthe brain and neck.
7. Echocardiogram: This creates a detailed image of theheart, which doctors can use to check for any sources ofclots that could have traveled to the brain.
Treatment
Strokes are a medical emergency and urgent treatment isessential.The sooner a person receives treatment for astroke, the less damage is likely to happen. It usuallytreated with medication. This includes medicines to preventand dissolve blood clots, reduce blood pressure and reducecholesterol levels.
Factors that influence stroke
1. Age, overall health, and past health.
2. Family history
Recovery
Speech therapy: This helps with problems producing orunderstanding speech. Practice, relaxation, and changingcommunication style can all make communicating easier.
Physical therapy: This can help a person relearn movementand coordination. It is important to stay active, eventhough this may be difficult at first.
Occupational therapy: This can help a person improve theirability to carry out daily activities, such as bathing,cooking, dressing, eating, reading, and writing.
Support groups: Joining a support group can help a personcope with common mental health issues that can occur after astroke, such as depression. Many find it useful to sharecommon experiences and exchange information. Support fromfriends and family: Close friends and relatives should tryto offer practical support and comfort after a stroke.Letting friends and family know what they can do to help isvery important. Rehabilitation is an important and ongoingpart of stroke treatment. With the right assistance and thesupport of loved ones, regaining a normal quality of life isusually possible, depending on the severity of the stroke.
Frequently Asked Questions About Stroke
During a stroke, bystanders should know the signs and act in time. If you believe someone is having a stroke — if the person loses the ability to speak, to move an arm or leg on one side, or experiences facial paralysis on one side — call 911 immediately. Stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate stroke treatment may save someone's life and enhance his or her chances for successful rehabilitation and recovery.
Ischemic strokes, the most common strokes, can be treated with a drug called tPA, which dissolves artery-obstructing clots. The window of opportunity to use tPA to treat stroke patients is small, so the sooner stroke patients can get to the hospital to be evaluated and receive treatment, the better their outcome. Stroke patients who receive tPA for their stroke symptoms are at least 30 percent more likely to recover from their stroke with less disability after three months than those who present to the hospital after three hours and are thus unable to receive tPA.
Stroke is a leading cause of serious, long-term adult disability. Four million Americans are living with the effects of stroke. The length of time to recover from a stroke depends on its severity. Fifty to 70 percent of stroke survivors regain functional independence, but 15 to 30 percent are permanently disabled.To reduce your risk of stroke, monitor your blood pressure, track your cholesterol level, stop smoking, exercise regularly, and find out if you should be taking a drug to reduce blood clotting.
There are things you can do to lower your risk of stroke. High blood pressure increases your risk of stroke four to six times. Heart disease, especially a condition known as atrial fibrillation, can double your risk of stroke. Your risk also increases if you smoke, have diabetes, sickle cell disease, high cholesterol, or a family history of stroke.