An overview of Drug Allergy
What is a Drug allergy?
A negative physical response to a substance is referred to as a drug allergy. There are various types of hypersensitivity responses to medications, including immediate and delayed ones.
As soon as the drug reaches the body, anaphylactic reactions start to happen right away. The drug causes the immune system to react and produces particular IgE antibodies. (proteins made by the immune system to fight the drug). We refer to this as "sensitization."
The body attempts to get rid of the medication when it is taken again by releasing significant amounts of the chemical histamine, which is released by the IgE antibodies. Immune cells assist in fighting the drug during a delayed response.
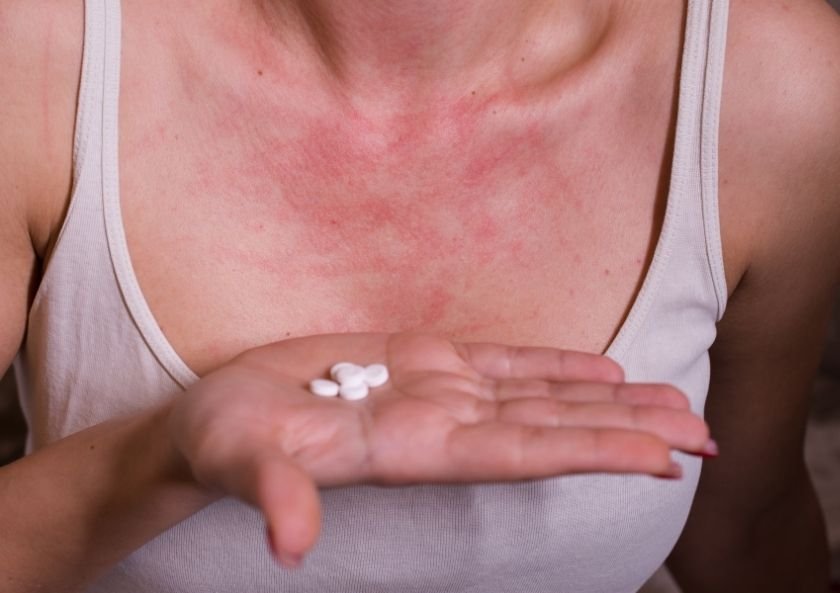
What are the symptoms of drug allergy?
Symptoms of a serious drug allergy often occur within an hour after taking a drug. Other reactions, particularly rashes, can occur hours, days or weeks later. Drug allergy symptoms may include:
1.Skin rash and hives
2.Itchy, watery eyes
3. Runny nose
4. Wheezing
5. Shortness of breath
6. Swelling
7. Fever
8. Itching
What causes drug allergy?
When your immune system misinterprets a medication as a dangerous substance like a virus or bacteria, it develops a drug allergy. Your immune system creates an antibody that is unique to a drug once it recognizes it as a potentially harmful substance. This can occur the first time you take a medication, but an allergy may not always manifest until several encounters.
These particular antibodies mark the drug and direct immune system attacks against it the following time you consume it. The symptoms of an allergic reaction are caused by chemicals released during this exercise.
However, you might not be conscious of when you first used drugs. According to some research, traces of a medication, like an antibiotic, in food may be enough to trigger the immune system to produce an antibody against it.
A slightly different mechanism may cause some allergic reactions. Some medications may be able to physically bind to the T cell, a specific type of immune system white blood cell. When you take the medication for the first time, this incident can release chemicals that can cause an allergic response.
How are drug allergies diagnosed?
A physician must thoroughly examine the patient's medical background and symptoms in order to identify drug allergies. Your dermatologist may perform a skin test to determine whether you are allergic to an antibiotic like penicillin if you have a suspicion that you are.
Skin testing, though not always accessible and occasionally risky, is not available for all medications. Your allergen may suggest a "challenge" in certain circumstances. (taking the medication again under medical supervision).
Your doctor may suggest using an alternative, equally effective drug if you have ever experienced a severe, life-threatening, allergic-type reaction to a specific medicine due to the risk involved with a reaction.
How are drug allergies treated?
The primary concern when treating drug allergies is relieving the symptoms:
Antihistamines and rarely corticosteroids can often alleviate common symptoms like rash, hives, and itching.Bronchodilators (inhalers), which relieve coughing and lung congestion, may be prescribed.Epinephrine (adrenaline) is typically given for more severe anaphylactic symptoms (life-threatening reactions, including difficulty breathing or loss of consciousness).
Desensitization is sometimes used to treat medication allergies, especially when testing is neither possible or practical. As long as you keep taking the prescription, this method aims to temporarily enable your body to tolerate allergens.
For instance, during penicillin desensitization, progressively greater doses of penicillin are given at intervals until your immune system becomes accustomed to the medication. Desensitization techniques do not treat medication allergies.
What drugs cause the most drug allergies?
Different drugs have different effects on people. That said, certain drugs do tend to cause more allergic reactions than others. These include:
1. antibiotics such as penicillin and sulfa antibiotics such as sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim
2. aspirin
3. nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen
4. anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine and lamotrigine
5. drugs used in monoclonal antibody therapy such as trastuzumab and ibritumomab tiuxetan
6. chemotherapy drugs such as paclitaxel, docetaxel, and procarbazine